
An experimental design includes subjects measured before and after a particular treatment, the sample population may be very small and purposefully chosen, and it is intended to establish causality between variables. A descriptive study is governed by the following rules: subjects are generally measured once the intention is to only establish associations between variables and, the study may include a sample population of hundreds or thousands of subjects to ensure that a valid estimate of a generalized relationship between variables has been obtained. Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.īefore designing a quantitative research study, you must decide whether it will be descriptive or experimental because this will dictate how you gather, analyze, and interpret the results. Colorado State University Singh, Kultar. Sharpe, 2008 Quantitative Research Methods. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011 McNabb, David E. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010 Brians, Craig Leonard et al. NOTE: When using pre-existing statistical data gathered and made available by anyone other than yourself, you still must report on the methods that were used to gather the data and describe any missing data that exists and, if there is any, provide a clear explanation why the missing data does not undermine the validity of your final analysis.īabbie, Earl R.

Explain your handling of missing data and why any missing data does not undermine the validity of your analysis.
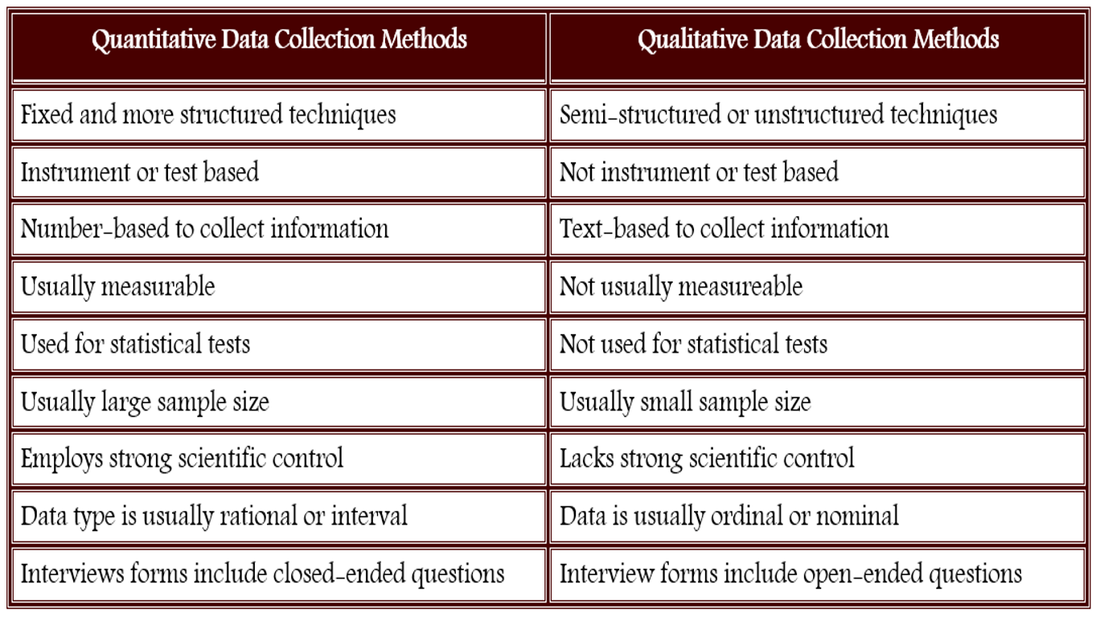
Explain how the actual analysis differs from the planned analysis. Report unanticipated events that occurred during your data collection.Interpretation of results is not appropriate in this section. Explain the data collected and their statistical treatment as well as all relevant results in relation to the research problem you are investigating.Things to keep in mind when reporting the results of a study using quantitative methods: The overarching aim of a quantitative research study is to classify features, count them, and construct statistical models in an attempt to explain what is observed. The researcher uses tools, such as questionnaires or computer software, to collect numerical data.Project can be used to generalize concepts more widely, predict future results, or investigate causal relationships.Data are in the form of numbers and statistics, often arranged in tables, charts, figures, or other non-textual forms.All aspects of the study are carefully designed before data is collected.The researcher has a clearly defined research question to which objective answers are sought.The research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given its high reliability.The results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the population.The data is usually gathered using structured research instruments.Quantitative research focuses on numeric and unchanging data and detailed, convergent reasoning rather than divergent reasoning. Quantitative research deals in numbers, logic, and an objective stance. A descriptive study establishes only associations between variables an experimental study establishes causality. Quantitative research designs are either descriptive or experimental . Your goal in conducting quantitative research study is to determine the relationship between one thing and another within a population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
